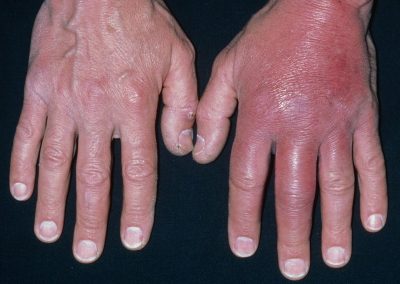
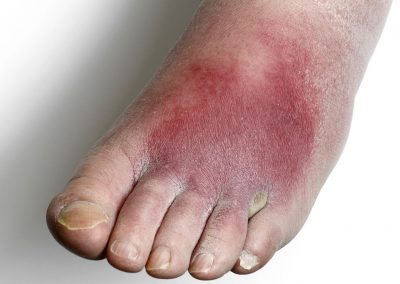
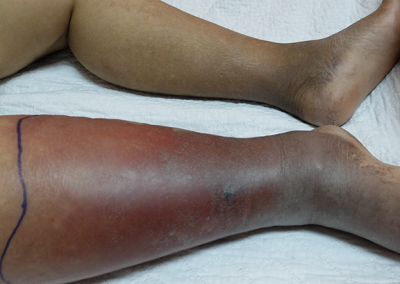
3 Reasons EVERYONE should have emergency medications avaiable. It's all about access—access to medications and care when you need it most. And when things happen outside of your control that access can disappear.Below are 3 examples of how easily this access can be...
Is intermittent Fasting Good for Weight Loss?

Over the past decade, intermittent fasting, also known as time restricted fasting, has gained popularity as a way to lose weight and mitigate health risks. Some of this is true, however as with all things that seem too good to be true there are a few things that intermittent fasting can do and a few things it can’t do.
Before you jump on the intermittent fasting bandwagon for either health or weight loss related reasons there are a few things to consider. It is true that intermittent fasting can help lower insulin levels and regulate blood sugar. It can help with appetite suppression and accelerate healing and lower inflammation. However, intermittent fasting isn’t for everyone. As far as weight loss is concerned, consistent lifestyle changes over a period of time, along with time restricted eating schedule has proven to help with weight reduction.
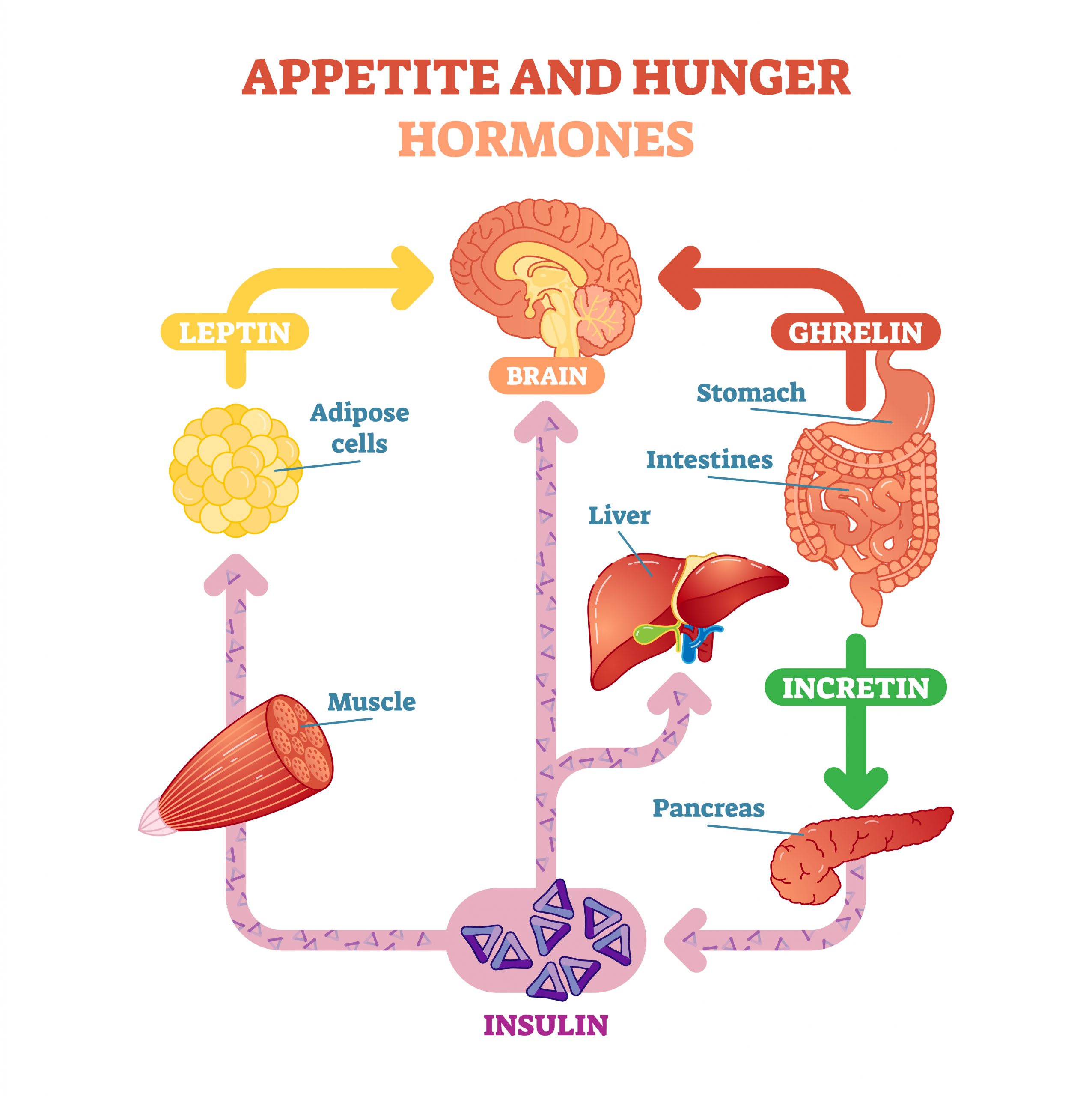
Terms
Leptin– Leptin is known as the appetite suppressant hormone. It is secreted by fat cells in response to an increase in insulin. In a healthy feedback loop, leptin decreases hunger.
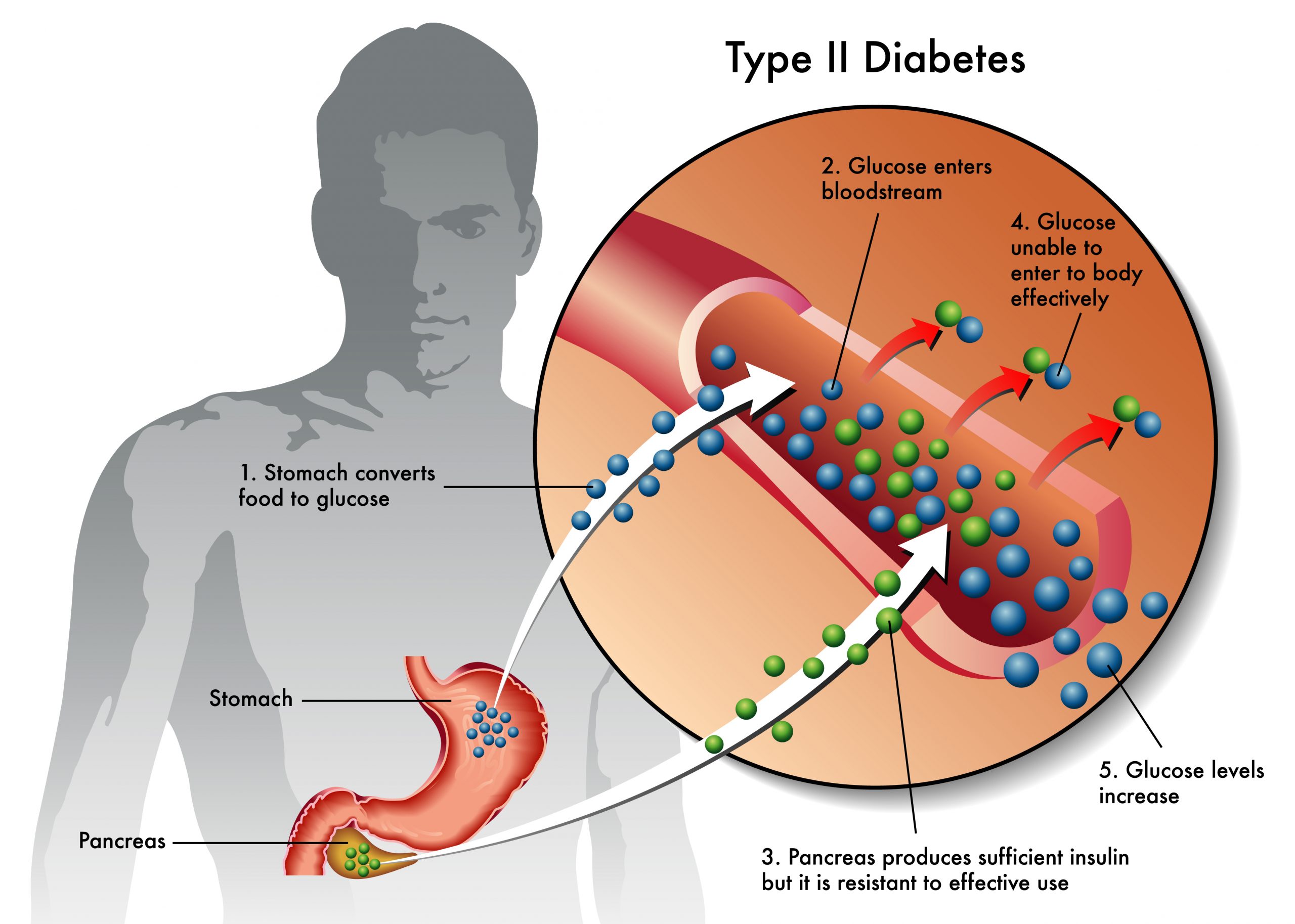
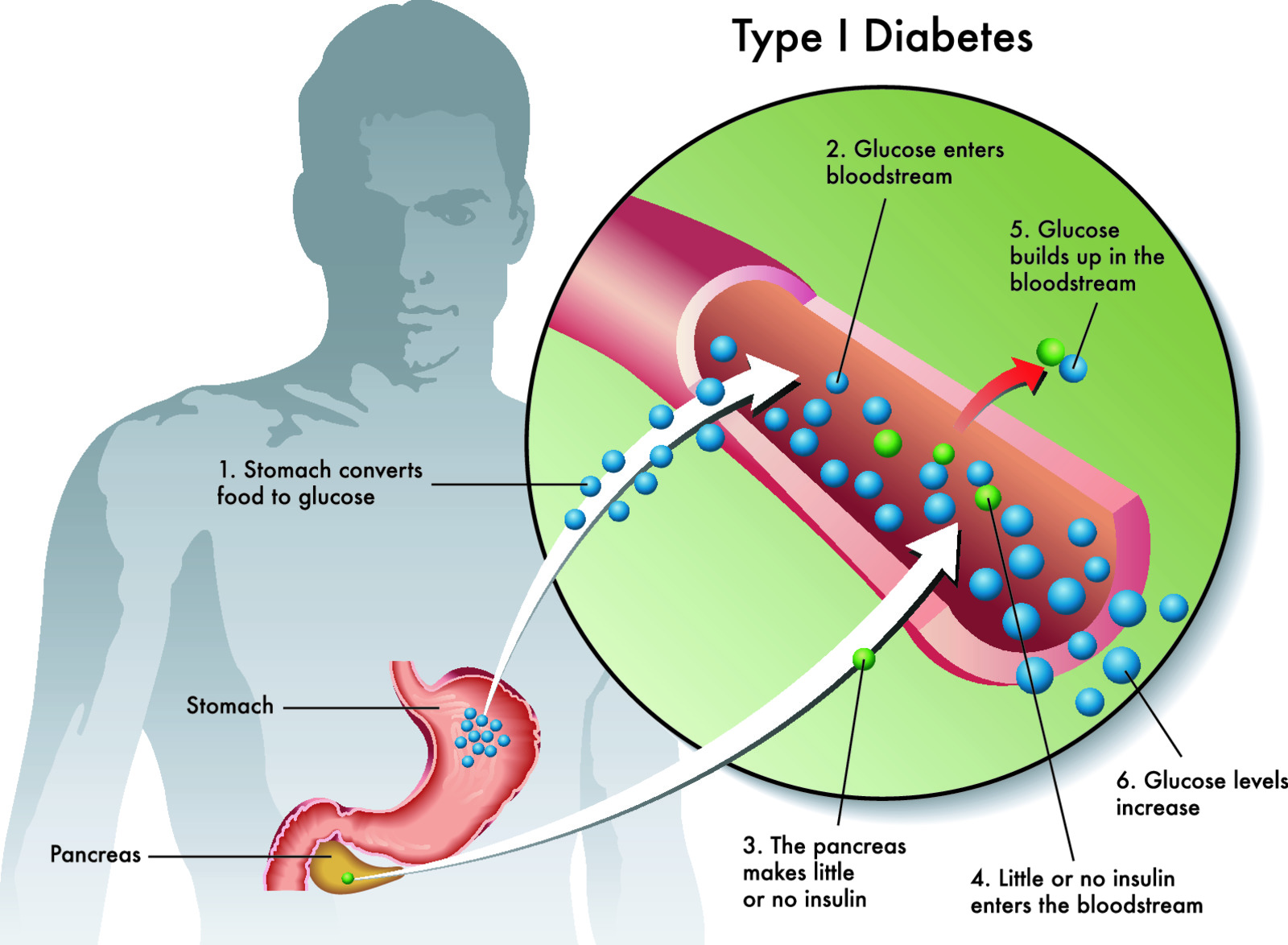
Insulin–Insulin is released by beta cells in the pancreas in response to increased blood glucose levels. In a healthy feedback loop, insulin acts like a gatekeeper by attaching to cells and allowing glucose into the cell, thereby providing energy to the cell.
Ghrelin– Ghrelin, also known as the hunger hormone, is primarily secreted in the stomach and gastrointestinal when your stomach is empty. It tells your brain you are hungry. It also regulates insulin secretion and has a role in reducing energy expenditure. Research continues to discover many other roles that ghrelin plays in the body.
Incretin- Incretin hormones are gut peptides that are secreted after nutrient intake and stimulate insulin secretion together with hyperglycemia. GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) und GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) are the known incretin hormones from the upper (GIP, K cells) and lower (GLP-1, L cells) gut.
The healthy leptin insulin feedback loop
In a healthy feedback loop, insulin levels rise due to food intake (which increases blood glucose), triggering fat cells to release leptin. Leptin reduces appetite. In turn, less or no food is eaten, resulting in lower blood glucose, which stabilizes insulin levels.
The unhealthy feedback loop
Persistent high levels of leptin cause cells to not be receptive to the effects of leptin. You continue to be hungry. The leptin, which is stored in your fat cells, doesn’t respond to feelings of satiety and you continue to be hungry. Insulin resistance is caused by persistent high levels of insulin. Cells don’t have gatekeepers(insulin)that allow glucose(energy) into the cell. This results in high circulating blood glucose levels.
Understanding the body weight thermostat
In a healthy feedback loop, the body weight thermostat sets the metabolism by the balance of the insulin-leptin feedback loop. Leptin goes up (reduce hunger) in response to rising insulin levels. This in turn lowers insulin levels because you aren’t eating. In this example, healthy body weight is maintained.
However, the body weight thermostat can malfunction. This happens when increased insulin levels- insulin levels that are increased over a period of months or years, cause insulin resistance. This results in weight gain.

Intermittent fasting/time restricted eating can balance insulin and blood sugar levels- if done right
Insulin is a primary driver of weight gain in many individuals. Correcting the imbalance through diet, exercise, reduced stress, and good quality sleep can reverse insulin and leptin resistance. It takes time, perseverance, education and planning to achieve optimum health and weight.
Talk with your healthcare provider before starting any time restricted fasting. Children, endurance athletes, underweight people, and women who are trying to conceive, pregnant, or breastfeeding should avoid intermittent fasting.
Fasting benefits and considerations
How and when to fast
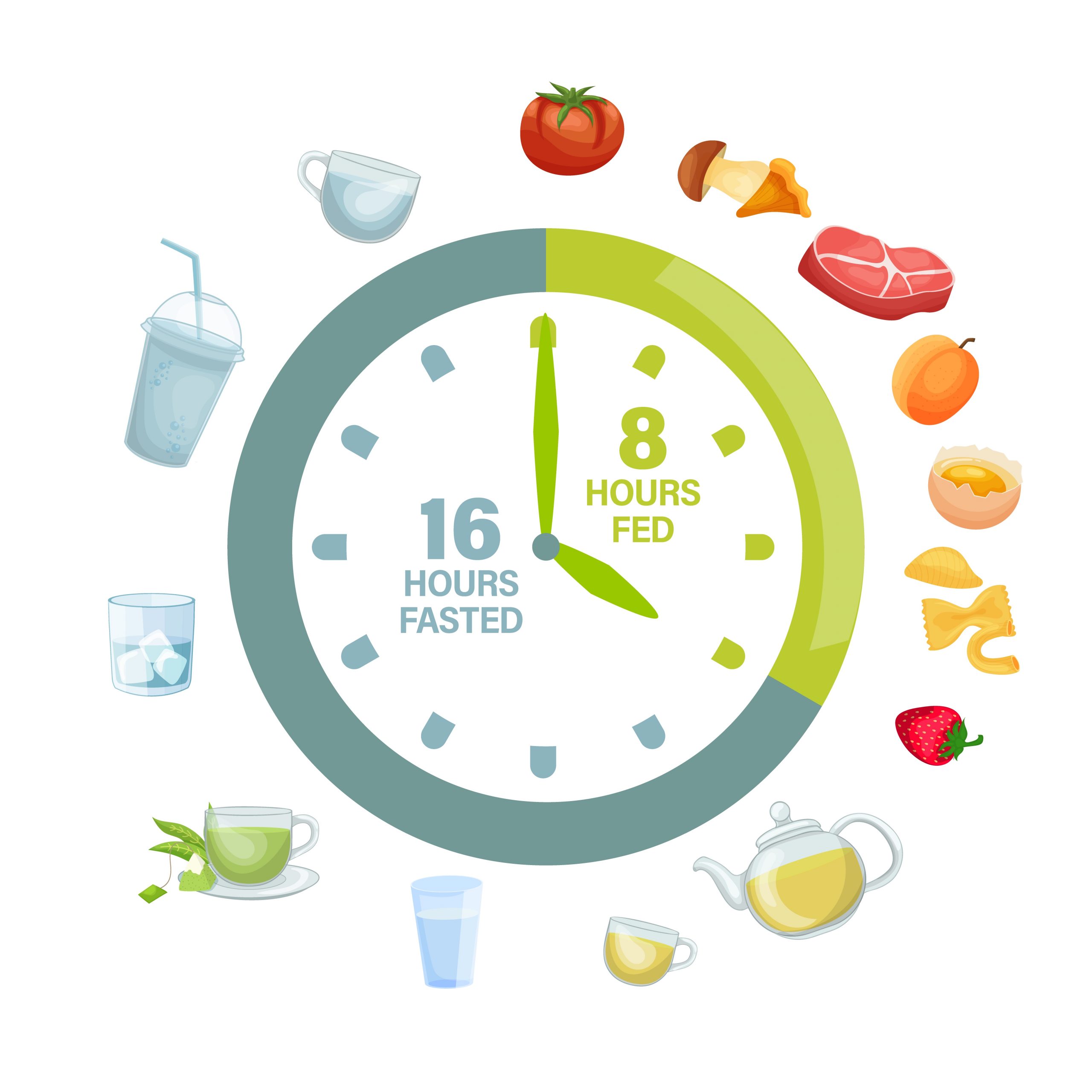
Research shows that a 16 hour fast with 8 hour eating schedule provides the body with enough time to reset insulin levels, reduce inflammation and help the body turn fat into energy in a process called ketosis. However, it can take a while to get to that eating window. Many people start with a 10 hour fast and gradually work up to the 16/8 schedule. However, there are many ways to do intermittent fasting. Some do alternate days fasting, others have a more time restrictive fasting window. It all depends on your schedule and health status.
There are many benefits to intermittent fasting. During a state of fasting the body has energy to repair since energy isn’t being used for digestion. In addition, human growth hormone (HGH) increases dramatically, which can facilitate fat burning. Inflammatory markers, which cause many health-related problems, such as heart disease and diabetes. Increases levels of BDNF, a brain hormone called brain-derived neurotrophic factor, in which a deficiency has been implicated in depression and other psychiatric illnesses.
New research out of Yale University discovered an enzyme (OGT) produced in the hypothalamic region of the brain regulates the body’s homeostatic set point body weight and lipid metabolism. The enzyme, OGT, significantly increased after 24 hour fasting period in mice, leading researchers to speculate this enzyme may have use in obesity prevention.
Intermittent fasting, cortisol, and stress
Any type of stress the body experiences- whether emotional or physical increases cortisol levels.
Cortisol prepares your body to deal with stressful situations by diverting resources, such as blood sugar or glucose, to give your body the energy it needs to respond to a stressor or crisis. Cortisol raises blood sugar levels, even during periods of fasting. This can lead to storing more fat, Once the body adjusts to time restricted eating, many of these stressors will more than likely start to disappear.
Intermittent fasting and thyroid hormones
The thyroid gland, releases several hormones that regulate metabolism. Intermittent fasting can lower T3 and T4 levels, which can actually lead to weight gain. This is usually solved by a gradual lengthening of the fasting period. Since the thyroid hormone needs glucose to convert from inactive to active hormones (T4 to T3) the transition to using ketones as fuel (which form after extended time of fasting) can be a challenge. Seek professional guidance when dealing with thyroid dysfunction, either hypo or hyperthroid.
Effects of Intermittent Fasting on reproductive hormones
Hypothalamic Kisspeptin neurons and their receptors are involved with puberty and reproductive hormone regulation. During fasting, these hormones are decreased and can affect fertility.
- Brooke Lounsbury, RN
Medical Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
Be Prepared for Life’s Unexpected Moments
Youth Preparedness: Teaching, Building, and Coping with Disasters
Educating and preparing your children ahead of time means fewer surprises in the event of an emergency.Growing Up Prepared: Empowering Youth in Disaster Preparedness As we observe National Preparedness Month, it's crucial to remember that disasters can strike at any...
Low-Cost and No-Cost Emergency Preparedness Measures
Small steps today, mean a safer tomorrow for you and your loved ones.Low-Cost and No-Cost Emergency Preparedness So far in our series for National Preparedness Month this September, we've already covered How to Make an Emergency Plan for Your Household and How to...