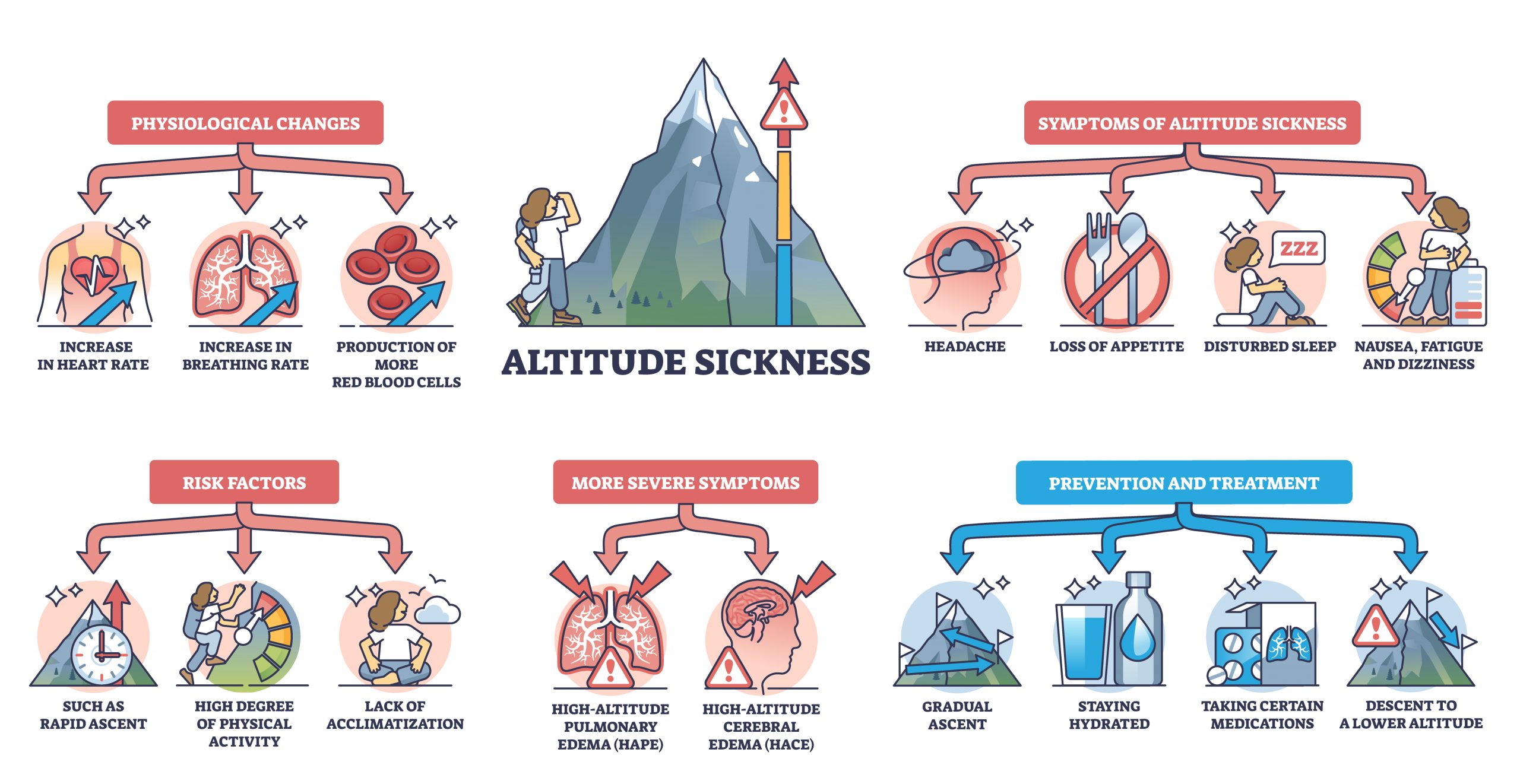
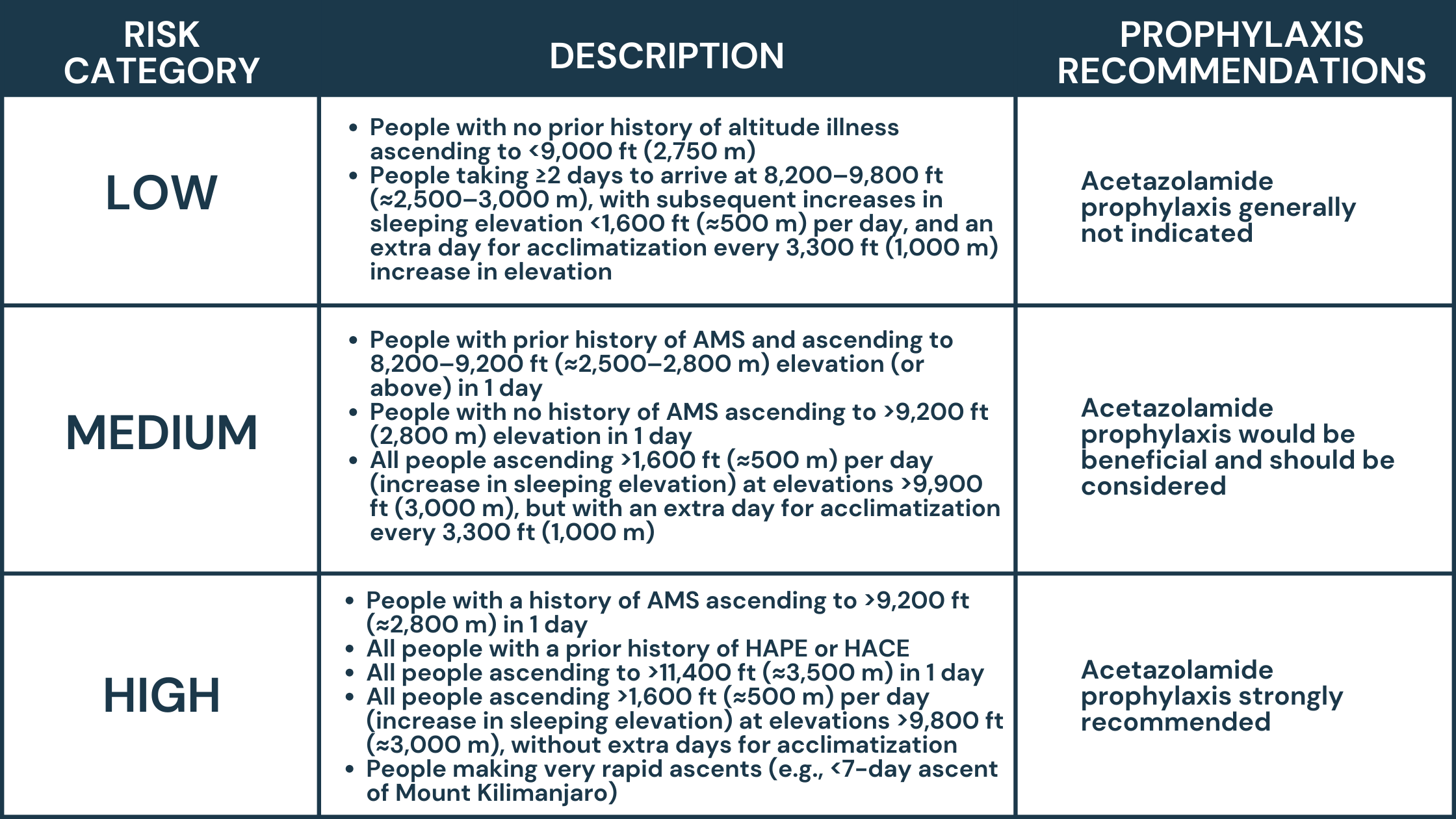
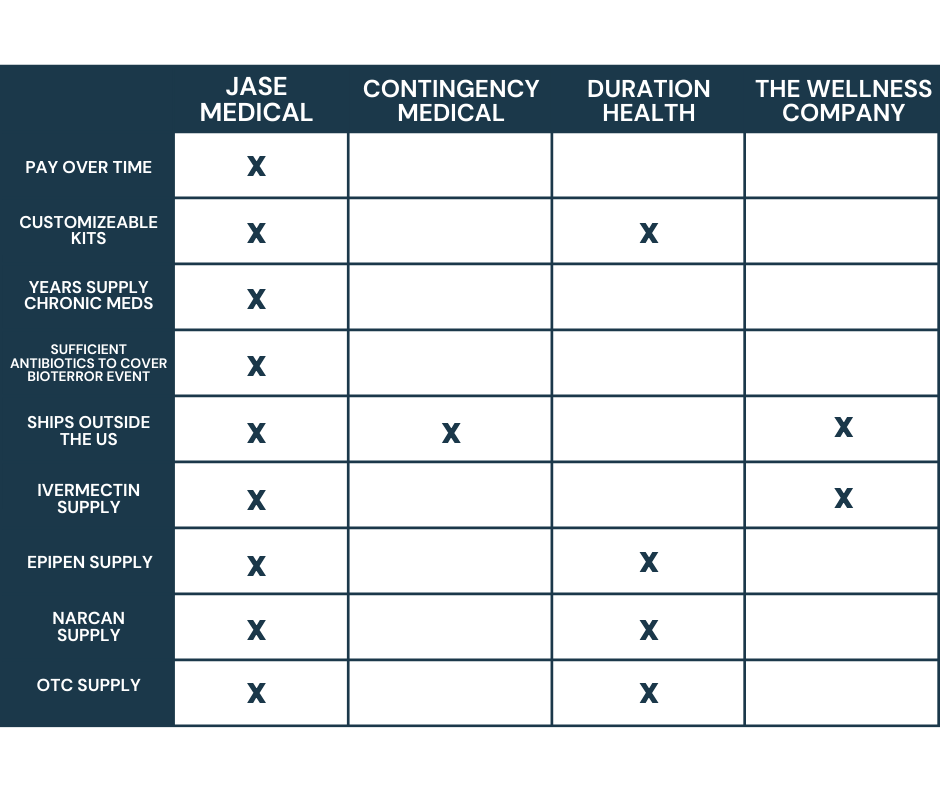
“Never go to a doctor whose office plants have died.”~ Erma Bombeck, humorist and author.Laughter is said to be the best 'chronic prescription' that our Jase Daily service aims to provide. If only. But combining laughter, positive thoughts, and having a purpose in...
Ivermectin for Scabies- and More
Discovered in the late 1970s and approved as a commercial product for animal health in 1981, ivermectin, an antiparasitic drug was initially used by veterinarians to treat mite and heartworm infections.
In 1988, ivermectin was approved to treat Onchocerciasis (known as river blindness) in humans.
Origins in Japanese Soil
Under the guidance of Satoshi Omura (former head of the Antibiotics Research Groupof Kitasato University) his team isolated a strain of Streptomyces avermitilis from a fermented a sample of Japanese soil. Merck Research Labs parasitology specialist, Willima C. Campbell began testing samples as a potential treatment for parasitic worms. The Streptomyces avermitilis strain was isolated. The group of drugs isolated is called a avermectins. From this group, eight different structures, including ivermectin, were isolated, and modified. It was discovered that ivermectin was 25 times more potent than existing treatments for parasitic worms.
Avermectins possess anticancer, anti-diabetic, antiviral, antifungal, and are used for treatment of several metabolic disorders.
Nobel Prize Awarded
Omura, along with Merck Research Labs parasitology specialist, William C. Campbell were awarded the 2015 Nobel Prize in medicine for developing ivermectin. As part of two global disease elimination campaigns, Ivermectin was responsible for lowering the incidence of river blindness and lymphatic filariasis, both caused by parasitic worms. Dubbed a “Wonder drug”, Ivermectin proved to be a safe, effective, and well tolerated drug. It is now being distributed and used free of charge in campaigns to eliminate both diseases globally which have devastated the world’s poor. It quickly became used to treat other parasitic conditions, from hookworms, roundworms, ear mites and scabies.
The Many Uses For Ivermectin
As a broad spectrum antiparasitic medication, ivermectin is included in the World Health Organizations Essential Medicines List.
Scabies– are microscopic mites that can live on your skin for months. It is a highly contagious condition that is spread through direct skin contact. The distinctive, raised rash may be skin color, red, brown or violet depending on skin tone.
Initial exposure can take 2-5 weeks to manifest symptoms. If prior exposure to scabies, symptoms can manifest in as little as 4 days.
Symptoms include intense itching, rash, hives or bumps under the skin. The burrow tracks can be seen on the skin as thin, raised discolored lines.
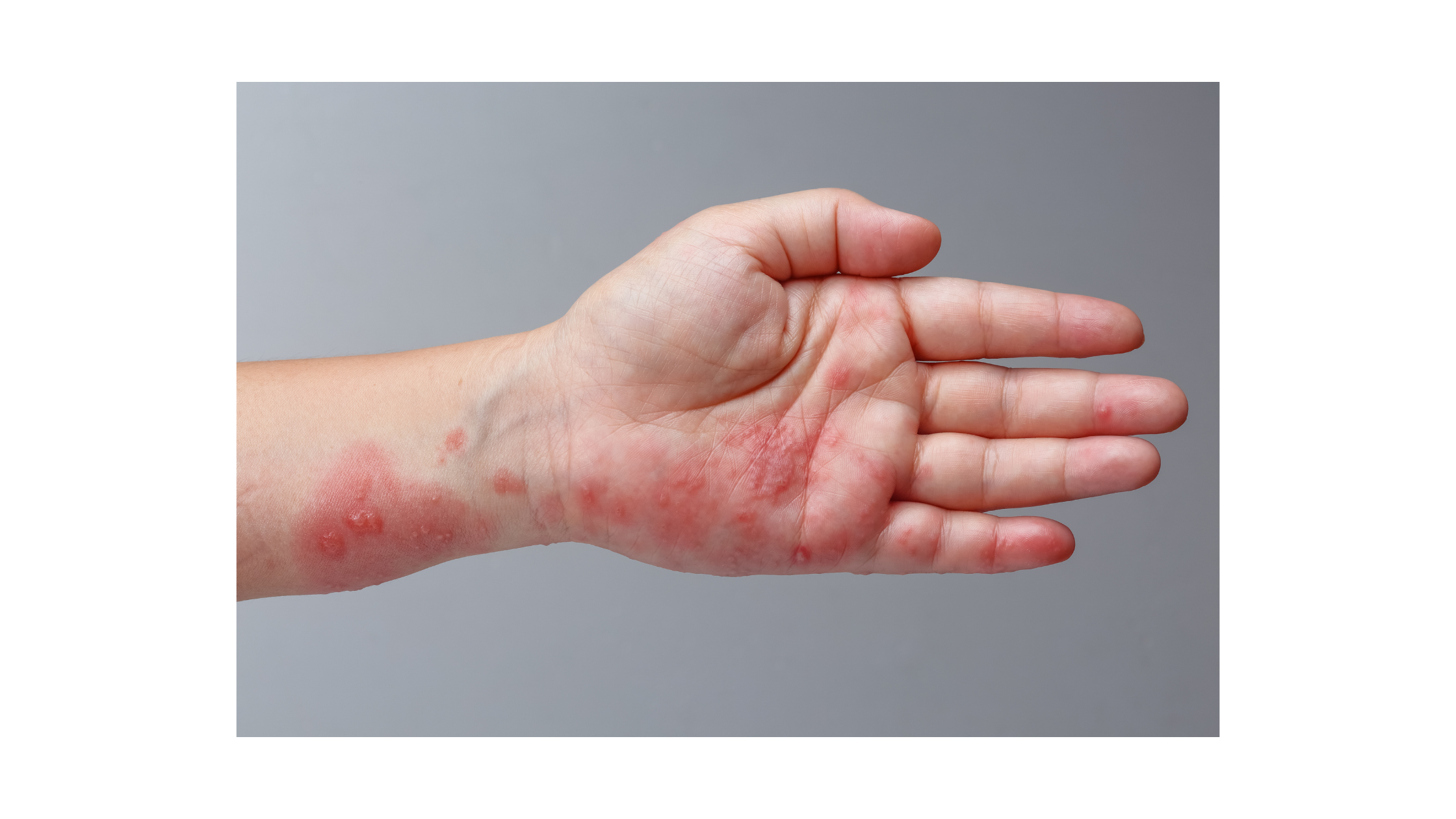
Common sites for scabies rash to appear include the wrist, elbow, armpit, nipple, penis, buttocks, waist and area between the fingers.
Side effects of ivermectin, although uncommon, include fever, itching, and skin rash.
There are several drugs that interact with ivermectin. Check out these drug interactions here.
Pregnant women are told not to take ivermectin due to its potential effect on the fetus.
Ivermectin is one of the medications found in the Jase add on list that you may add to your Jase Case.
Powerful Antiviral Against Many Viruses
In addition, the antiviral activity of Ivermectin has been shown to be effective against a wide range of RNA and DNA viruses, for example, dengue, Zika, yellow fever, and others.
Off Label Use- Covid 19
The CDC, FDA and World Health organization do not recommend ivermectin as a treatment for Covid-19 unless ivermectin is used in a research setting, as part of a clinical trial.
However, a meta-analysis published in the American Journal of Therapeutics (July/August2021 edition) titled, “Ivermectin for Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Trial Sequential Analysis to Inform Clinical Guidelines” reviewed and analyzed 15 trials found that ivermectin reduced the risk of death compared with no ivermectin. (See paper here).
Ivermectin is considered to be one of the world’s most valuable and lifesaving drugs and has earned a place alongside penicillin for its impact on saving lives.
- Brooke Lounsbury, RN
Medical Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
Two Simple Ways to Enhance Your Well-being Alongside Medication
Why Do People Want a 12-Month Supply of Their Prescription Medications?
There are a lot of things we like to stock up on: pressure-canned fruits and vegetables, canned goods at the grocery store. (“Two for a dollar?! I need another cart!”), soaps and cleaners . . .And toilet paper! Oh yes! But stock up on prescription medicines for months...
Navigating Spring’s Waters: Hydration, Recreation, and the Risk of Giardia
Even crystal clear water can conceal hidden hazards. .Spring Brings water, water brings risks. With spring in full swing and temperatures rising, our thirst (pun intended) for water grows as well. This applies to both the need to stay hydrated and the desire to cool...
The Importance of Timely Antibiotic Intervention
Accelerate healing through early treatment. .The Key to Effective Infection Management: Early antibiotic intervention and at the right dose. While aggressive antibiotic treatment with high dosages has been the go-to methodology of treatment historically, research by...