
There is confusion surrounding vitamin K. We know vitamin K as the clotting vitamin, found in large amounts in leafy green vegetables. When someone is on blood thinners they are usually cautioned about their intake of greens and how it can interfere with the effectiveness of the medication. But did you know there is a vitamin K1 and K2?
There are two forms of vitamin K, K1 and K2
Vitamin K is the generic name for a family of similar compounds that are fat soluble, are found in food and are also found in supplement form. These compounds include phylloquinone (vitamin K1) and a series of menaquinones also known as MKs (vitamin K2). Vitamin K2 can be divided into subtypes: short-chain (i.e., menaquinone-4; MK-4- most bioavailable) and long-chain (MK-7, MK-8, and MK-9)
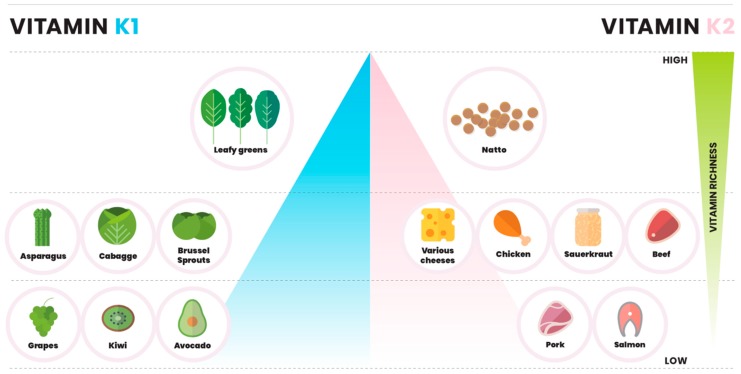
Vitamin K1 is found in spinach, cabbage, and kale. K1 can also be found in fruits like avocado, kiwi and grapes. Absorption of K1 is increased when eaten with fat, such as butter or oils.
Vitamin k2 is found in fermented food (sauerkraut and vegetables), meat, and dairy. Other sources of K2 are chicken meat, egg yolks, beef and salmon. K2 is synthesized by bacteria, and a small amount is produced by the bacteria in the gut. Absorption is also increased when eaten with fats such as butter or oils.
Health benefits of both vitamin K1 and K2
Both vitamin K1 and K2 are vital to health. They work in drastically different ways and on different parts of the body. About 10-15% of vitamin K1 is absorbed by the body compared to 50% of vitamin K2. The Standard American Diet (SAD) intake of vitamin K1 is higher than K2.
- Assists with bleeding and bruising regulation in the body
- Acts as an anti-inflammatory and protects against oxidative stress
- Is a cofactor to make prothrombin ( clotting factors)
- Precursor to K2
- Bone health
- Prevents arterial calcification
- Assists with blood clotting in similar way as K1
- Anti cancer effects on leukemia, , hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), lung cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer and colorectal cancer
- Improves insulin resistance
- May help prevent bone fractures, especially in post menopausal women
Factors that prevent absorption of vitamin K absorption
- Health problems that can prevent your body from absorbing vitamin K, such as gallbladder or biliary disease, cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, and Crohn’s disease
- Liver disease
- Taking blood thinners, such as warfarin (Coumadin)
- Long-term hemodialysis
- Serious burns
- Consumption of trans fats (k2 absorption)
- Broad spectrum antibiotic use (k2 absorption)
- Dilantin
- Fat blocking medications such as Orlistat
- Brooke Lounsbury, RN
Medical Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
FAQ: Our most commonly asked questions about Jase
If you’re considering Jase, chances are you’ve paused and thought, “This makes sense, but I still have a few questions.”You’re not alone. Here are the most common ones we hear, answered plainly. Is this really doctor-prescribed? Yes. Every Jase order is reviewed by a...
Medical Readiness: What Really Kills First
When Disaster Strikes, It’s Not Hunger or Thirst That Takes the First Lives In every disaster zone, from hurricanes in the Caribbean to war zones in Ukraine, the pattern is the same. People worry about food and water, but it’s infection that kills first. A small wound...
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole *Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional guidance.* In the evolving...



