When Disaster Strikes, It’s Not Hunger or Thirst That Takes the First Lives In every disaster zone, from hurricanes in the Caribbean to war zones in Ukraine, the pattern is the same. People worry about food and water, but it’s infection that kills first. A small wound...
Stop Ticks in Their Tracks: Prevention, Removal, and Treatment
Don’t get ticked off: Tips for how to conquer those tiny terrors.
Unfortunately we humans aren’t the only ones who enjoy the nice weather this time of year.
Ticks usually go dormant for the winter (unless they have found a warm, hospitable host), so we tend to let our guard down when it’s cooler, knowing that they aren’t as much of a concern. But that changes as soon as the weather does. They are most active from April to September, just when we’ll be outside enjoying the warmer weather. It’s feeding time for the ticks, and we’re on the menu.
Ixodida. That’s the scientific name for ticks. But you don’t need to know that to know how much you hate the little buggers. They are almost everywhere we go outdoors, but we often don’t know they are there until we find one on us – after we’ve been bitten.
| In the last dataset gathered (2017-2019) nearly 50,000 tick bites per year result in emergency room visits |
Let’s explore some ways to mitigate bites, and treat them if they do happen:
Start with prevention:
- Dress Smart: Wear long pants and sleeves, tucking pants into socks. Light-colored clothing makes spotting ticks easier.
- Tick Habitats: Avoid tall grass, brush, and leaf litter where ticks lurk. Stick to cleared paths when hiking.
- Repellent Power: Use an EPA-registered insect repellent containing at least 20% DEET on exposed skin (follow label instructions carefully). Consider permethrin for clothing (not directly on skin).
- Post-Adventure Check: After coming indoors, do a thorough full-body tick check, including in and around the hair, armpits, groin, and behind the knees.
Tick Removal 101:
If you find a tick attached:
- Don’t Panic: Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick firmly near its head (avoid squeezing the body). Pull straight up with steady, gentle pressure.
- Clean Up: Disinfect the bite area and your tweezers with rubbing alcohol or soap and water.
- Save the Evidence: Place the tick in a sealed container (alive or dead) for potential identification if needed.
Important Note: Resist the urge to burn, suffocate, or folk remedies for tick removal. These can irritate the bite and increase infection risk.
Seek medical attention if:
- The tick was attached for more than 24 hours (increases disease transmission risk).
- Part of the tick remains embedded in the skin.
- You experience a rash around the bite or flu-like symptoms within a few weeks.
It’s important to know your risks: Check to see if you live in a region where the Lyme disease carrying ticks are more abundant.
Treatment with Doxycycline:
- Effectiveness: Doxycycline is a first-line antibiotic treatment for Lyme disease, particularly in its early stages.
- Treatment Duration: The typical course of doxycycline for Lyme disease is 10-14 days, although it can be extended for more complex cases.
- Prescription Only: Doxycycline is a prescription medication and should only be taken under a doctor’s supervision.
- Not for Prevention: Doxycycline is for treating established Lyme disease infections, not preventing them after a tick bite.
Lyme disease is the most common vector-borne disease in the U.S. with between 20,000 and 30,000 confirmed cases each year.
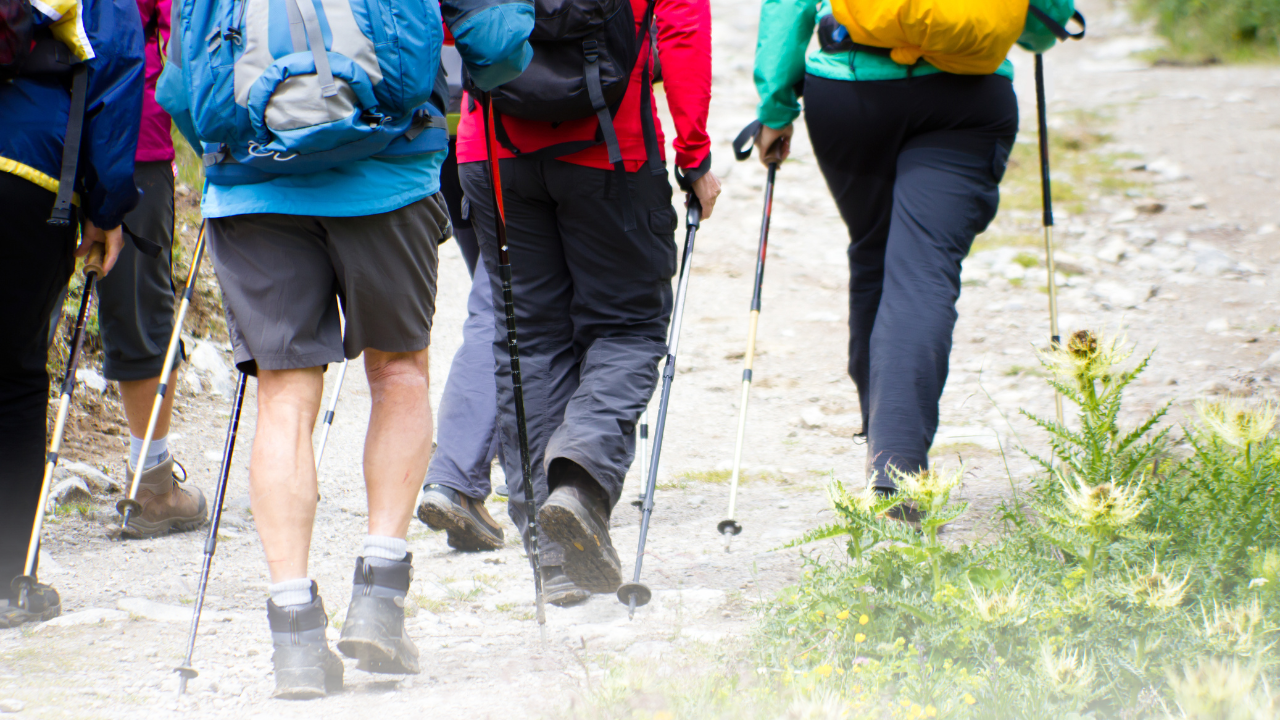

Remember, ticks live where we play!
Since ticks are likely to be wherever we’re spending time outdoors, it’s important to be mindful of their presence. But since our adventures often take us to remote places, it’s also important to have the medications you may need with you.
Doxycycline is just one of the 5 included life-save medications that come in every Jase Case – and it’s not only for Lyme disease. Doxy is also used to treat respiratory tract infections, dental infections, skin infections, certain STI’s, malaria, and even certain types of food poisoning.
Give yourself some peace of mind knowing you’re covered for all of the most common infections with a Jase Case.
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
Medical Readiness: What Really Kills First
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole *Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional guidance.* In the evolving...
Be Prepared for Life’s Unexpected Moments
3 Reasons EVERYONE should have emergency medications avaiable. It's all about access—access to medications and care when you need it most. And when things happen outside of your control that access can disappear.Below are 3 examples of how easily this access can be...
Youth Preparedness: Teaching, Building, and Coping with Disasters
Educating and preparing your children ahead of time means fewer surprises in the event of an emergency.Growing Up Prepared: Empowering Youth in Disaster Preparedness As we observe National Preparedness Month, it's crucial to remember that disasters can strike at any...