If you’re considering Jase, chances are you’ve paused and thought, “This makes sense, but I still have a few questions.”You’re not alone. Here are the most common ones we hear, answered plainly. Is this really doctor-prescribed? Yes. Every Jase order is reviewed by a...
Sepsis – A Medical Emergency
- At least 1.7 million adults in America develop sepsis.
- At least 350,000 adults who develop sepsis die during their hospitalization or are discharged to hospice.
- 1 in 3 people who dies in a hospital had sepsis during that hospitalization
- Sepsis, or the infection causing sepsis, starts before a patient goes to the hospital in nearly 87% of cases.
What is sepsis?
Sepsis is an extreme medical emergency in response to an infection that has triggered an immune response that causes extensive inflammation throughout your body. This can lead to tissue damage, organ failure and even death. Sepsis occurs when an infection in the body weakens the immune system, and the body stops fighting the infection. At the same time your body stops fighting the infection, your body develops blood clots, leading to reduced flow to organs. This leads organ failure and in some instances even death.
Many different types of infections can trigger sepsis, which is a medical emergency. The quicker you receive treatment, the better your outcome will be. Most cases of sepsis start as a bacterial infection. Some cases of sepsis are from viral or fungal infections.
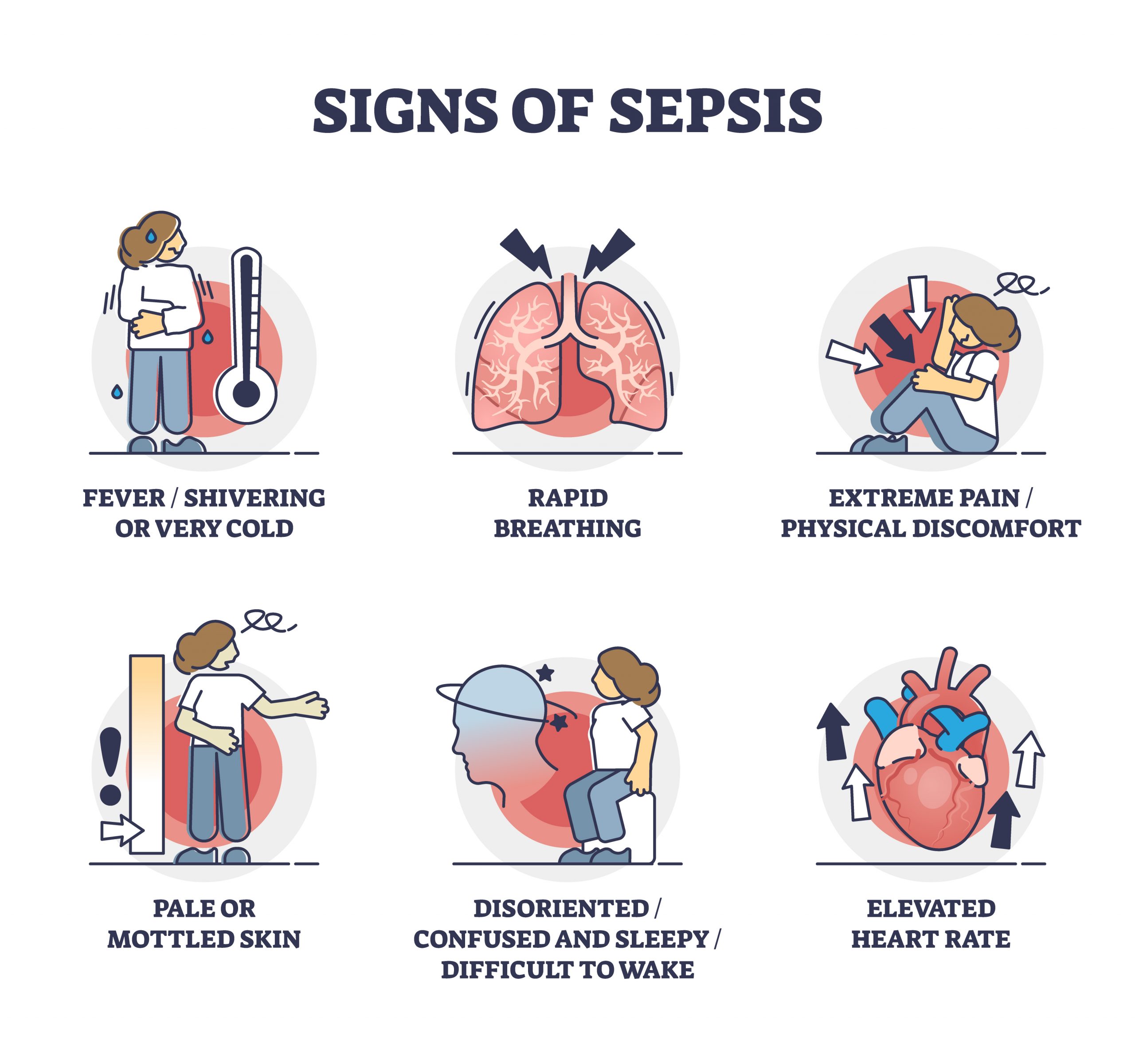
Symptoms of sepsis
The symptoms of sepsis are specific across populations, and can appear differently in children compared to adults- but can include:
- Fever and chills
- Very low body temperature
- Peeing less than usual
- Fast heartbeat
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue or weakness
- Blotchy or discolored skin
- Sweating or clammy skin
- Confusion, change in mental status
- Shallow breathing
Sepsis complications-if not treated or treatment started late
- Kidney failure
- Dead tissue (gangrene) on fingers and toes, leading to amputation
- Lung, brain, or heart damage
- A higher risk of infections over time
- Sepsis can be deadly in between 25% and 40% of cases.
Risk Factors for Sepsis
Anyone can get sepsis, however the following groups more at risk for developing sepsis:
- Over 65- as we age our immune systems weaken
- Infants, very young children, pregnant women
- People with indwelling catheters, along with respiratory devices, ports and IV sites-these are all entry points for infection.
- Severe, open injuries- or extensive burns
- Chronic conditions such as diabetes. Poorly controlled blood sugars feed infection. Other risk factors include cancer, lung disease, immune system disorders, and kidney disease.
- Dementia and Alzheimer’s patients are unable to express discomfort or pain and are at risk for urinary tract infections-which can lead to sepsis if not treated.
- Recently hospitalized or recent surgery
- On steroid therapy- steroids weaken immune system
Sepsis is most commonly associated with the following types of infections:
Note: Sepsis is NOT contagious
- Lung infections (like pneumonia)
- Urinary tract infections
- Skin infections (especially burns)
- Infections of the digestive system
Prevent infections by
- Practicing good hygiene- hand washing, keep infected wounds covered, wear gloves during dressing changes.
- Take care of chronic conditions- especially immune system disorders
- Diabetics are prone to infections- keep blood sugars under control
- In the case of Alzheimer’s and dementia patients monitor urine for obvious signs of urinary tract infection.
Prevent sepsis by:
- Monitoring any lung, urinary tract, wound or gastrointestinal infections and getting appropriate antibiotic therapy (if indicated) started before symptoms of sepsis emerge.
- A single oral dose of the antibiotic azithromycin can reduce the risk of postpartum sepsis and death among women who deliver vaginally by one-third, according to a large multi-country clinical trial funded by the National Institutes of Health. Azithromycin is one of the antibiotics in the Jase case- use only on the instruction of your care provider.
If sepsis is suspected
Seek emergency care immediately
Sepsis symptoms can develop and deteriorate rapidly
The sooner an intervention is started the higher your chance of survival. If sepsis symptoms are mild, you may be sent home with oral antibiotics. Two antibiotics that may be prescribed are supplied in the Jase case- azithromycin and ciprofloxacin.
If sepsis symptoms are severe, you will be admitted to the hospital, given IV fluids, blood pressure monitored, given vasopressors (to constrict blood vessels, which in turn raises blood pressure) and antibiotics along with other supportive therapy.
- Brooke Lounsbury, RN
Medical Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
FAQ: Our most commonly asked questions about Jase
Medical Readiness: What Really Kills First
When Disaster Strikes, It’s Not Hunger or Thirst That Takes the First Lives In every disaster zone, from hurricanes in the Caribbean to war zones in Ukraine, the pattern is the same. People worry about food and water, but it’s infection that kills first. A small wound...
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole *Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional guidance.* In the evolving...





