If you’re considering Jase, chances are you’ve paused and thought, “This makes sense, but I still have a few questions.”You’re not alone. Here are the most common ones we hear, answered plainly. Is this really doctor-prescribed? Yes. Every Jase order is reviewed by a...
The Ongoing Adderall Shortage


The ongoing Adderall shortage seems to have no end. Teva, the largest manufacturer of Adderall, is experiencing “ongoing intermittent manufacturing delays” due to increased demand. Every year, the DEA sets a quota — a limit on the amount of raw materials for many controlled substances, like Adderall. This is based in part on the Food and Drug Administration’s estimate of the need for the drug: For 2023, the FDA estimated just over 38,000 kilograms of amphetamine would be sufficient to meet the demand for Adderall and its generics – and the DEA set the quota at 42,400 kilograms, according to a DEA spokesman.
What is Adderall?
Adderall is a combination medication of Amphetamine/dextroamphetamine, used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder – ADHD (attention deficit hyperactive disorder) and narcolepsy, a sleep disorder that makes one drowsy and unable to stay awake during the day.
Adderall is classified as schedule ll drug because its potential for abuse is high, due to its addictive nature. Other drugs that fall in this category are Vicodin, cocaine, fentanyl, oxycodone and Ritalin.
The Adderall shortage is affecting a large part of the U.S. population
According to the CDC:
CDC scientists found that, as of 2016, 6.1 million children aged 2-17 years living in the U.S. had been diagnosed with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), which is similar to previous estimates. Researchers also found that children living in rural areas were more likely to have been diagnosed with ADHD and less likely to receive behavioral treatment in the past year compared with children living in urban or suburban areas.
Among all children 2-17 years of age with ADHD, researchers also found:
- 6 out of 10 (62%) were taking medication for their ADHD, and represent 1 out of 20 of all U.S. children;
- Just under half (47%) received any behavioral treatment for their ADHD in the past year. Among the youngest children (2-5 years of age), the number increased to over half (60%);
- Nearly two-thirds (64%) also had another mental, emotional, or behavioral disorder, such as conduct disorder, anxiety, depression, autism, and Tourette syndrome.
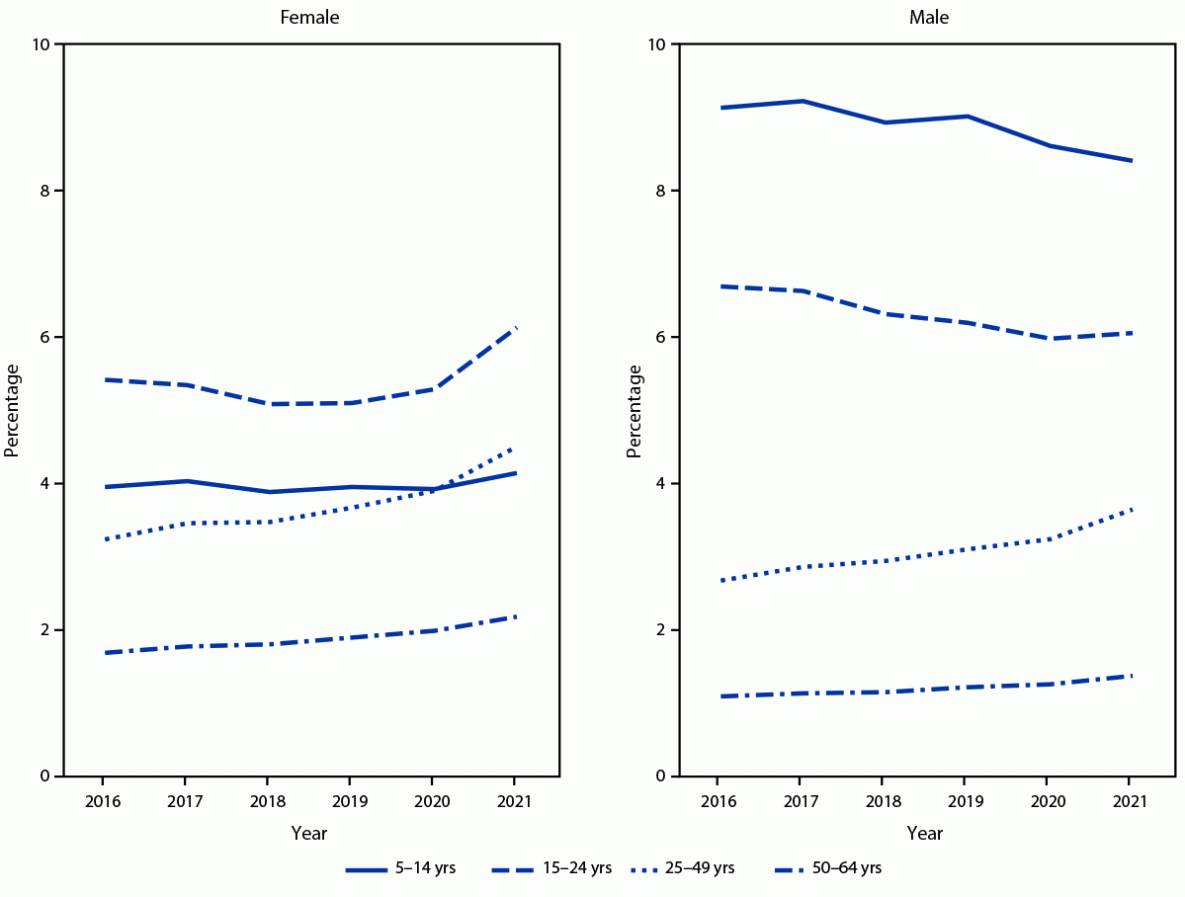
During the pandemic, prescriptions for ADHD medications increased significantly
Relative annual percent change in percentage of persons aged 5–64 years with at least one stimulant prescription fill, by sex and age group — MarketScan commercial databases, United States, 2016–2021
How Adderall works
It is a stimulant that works by increasing the amounts of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in the “reward” center of the brain. It is released during pleasurable activities such as eating, sex, regular exercise and any activity that involves expectation of reward.
Norepinephrine affects how the brain responds to events, particularly how it pays attention and the speed with which it reacts to outside stimuli., belongs to a class of drugs known as stimulants. It can help increase your ability to pay attention, stay focused on an activity, and control behavior problems. High levels of norepinephrine activate the “fight or flight” part of the sympathetic nervous system, leading to fear and anger responses.
What non pharmaceutical interventions you can do to increase dopamine and norepinephrine
There are a wide variety of treatments available for ADHD, including medication, counseling and behavior therapy, and lifestyle changes.
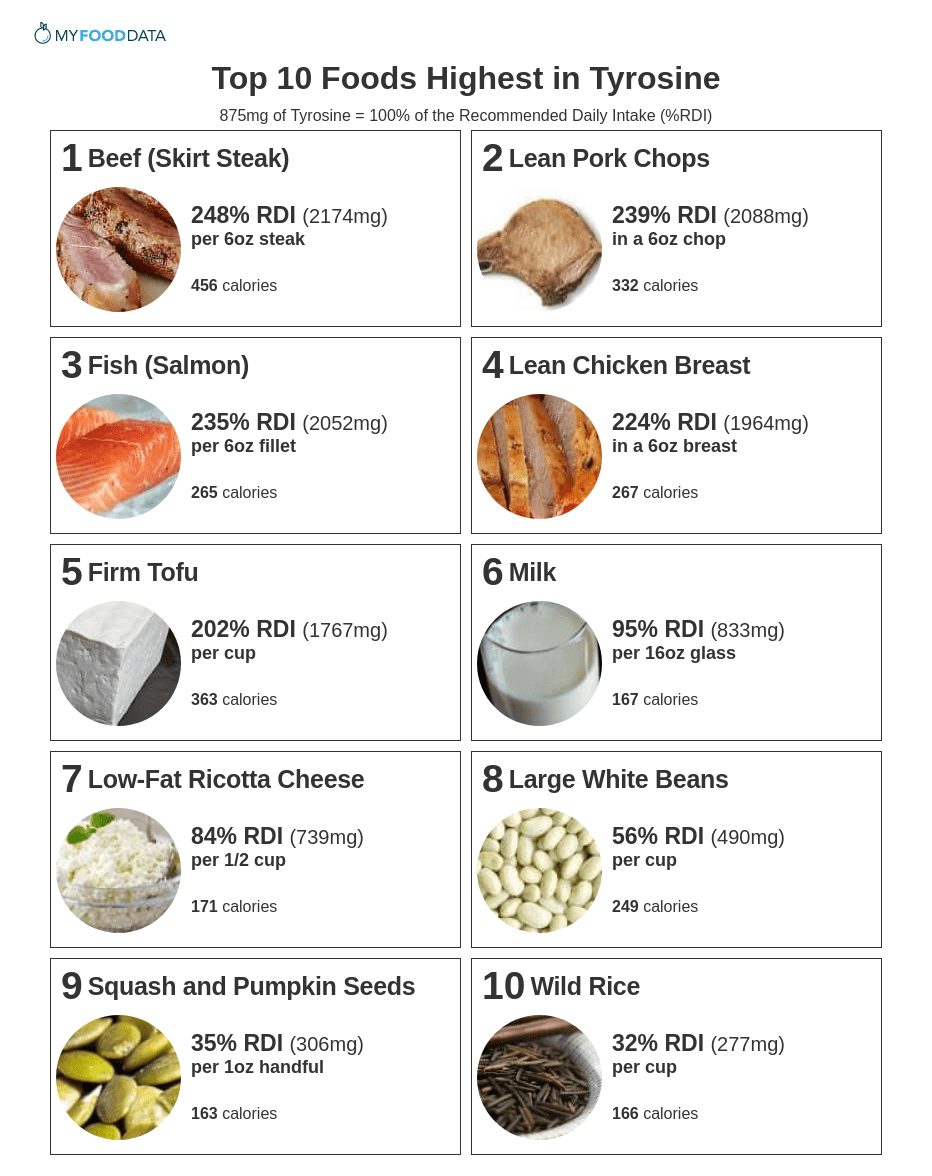
- Eat tyrosine rich foods
Tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid, meaning the body can synthesize it, and is a precursor to norepinephrine and increases dopamine availability. Tyrosine rich foods include:
Beef, pork, fish chicke4n, firm tofu, milk, low fat ricotta cheese, large white beans, squash and pumpkin seeds and wild rice
- Regular exercise
Regular, consistent exercise has been proven to increase dopamine levels in the brain. In addition, regular exercise is widely known to improve mood.
- Balance gut health
Recent research is proving the important role your digestive system has in producing many neurotransmitters, including dopamine. Healthy microbiota in the gut leads to dopamine, serotonin and other neurotransmitters increase. Fermented foods which are rich in probiotics, kefir,yogurt with active cultures and fiber rich fruits and vegetables contribute to overall health.
- Get good quality sleep
Sleep allows the body to repair and rejuvenate. Sleep is one of the most important and underrated activities we engage in. When rested, your body is able to hand stressors and remain more alert and focused.
- Practice meditation or prayer
According to a study “Increased dopamine tone during meditation-induced change of consciousness” two sets of participants were evaluated. One set had eyes closed, and not instructed to do anything. The other set practiced focused meditation. The focused meditation group had a 65% increase in endogenous dopamine release. An increase in dopamine also occurred during a 7-day spiritual retreat.
- Brooke Lounsbury, RN
Medical Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
FAQ: Our most commonly asked questions about Jase
Medical Readiness: What Really Kills First
When Disaster Strikes, It’s Not Hunger or Thirst That Takes the First Lives In every disaster zone, from hurricanes in the Caribbean to war zones in Ukraine, the pattern is the same. People worry about food and water, but it’s infection that kills first. A small wound...
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole *Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional guidance.* In the evolving...






