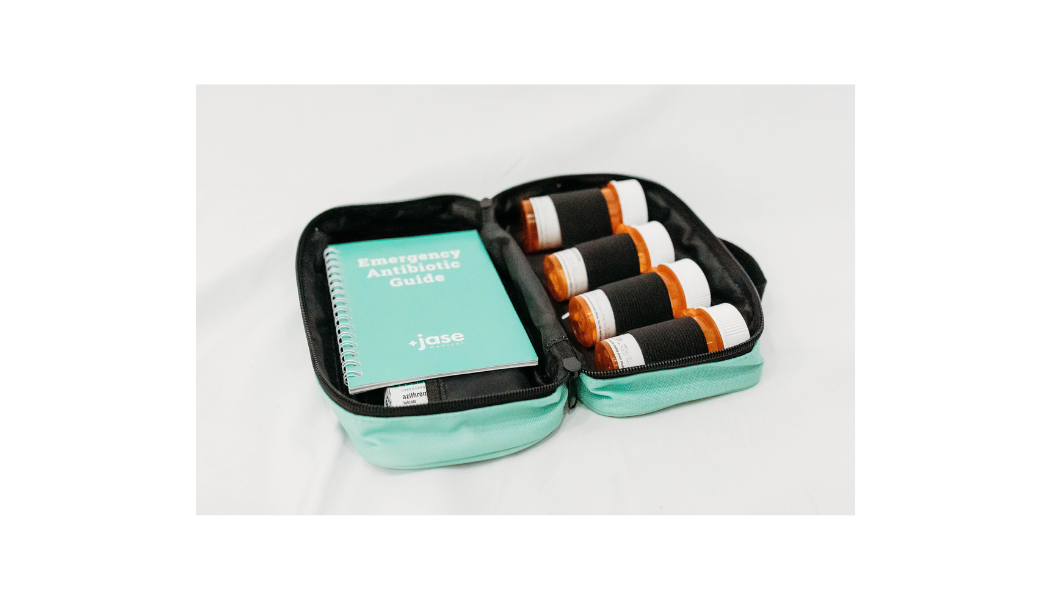
3 Reasons EVERYONE should have emergency medications avaiable. It's all about access—access to medications and care when you need it most. And when things happen outside of your control that access can disappear.Below are 3 examples of how easily this access can be...
Medical Care Without Insurance: 5 Affordable Ways to Obtain Healthcare

Getting the medical care that you need can be extremely expensive, even prohibitively so if you do not have any health insurance in place.
However, there are ways you access better medical care even if you don’t have health insurance. Not having insurance doesn’t mean having to skip the healthcare that you need.
These are the five resources that you should be aware of if you’re looking to find medical care without health insurance.
1. Connect With Local Resources
One of the first things you can explore are the local resources for healthcare.
A great place to start is through community programs that focus on medical treatment and healthcare. These can include local community hospitals, emergency centers, and even nonprofits in your community.
These places often feature sliding scale fees, accessible payment methods, and even payment plans that can help you handle the financial cost of medical care.
Do note that these programs often have lengthy wait lists, so it’s better to start your search sooner rather than later.
Try booking an appointment ahead of time rather than waiting till the last minute to get the care that you’re looking for.
2. Opt for Generics Over Brands

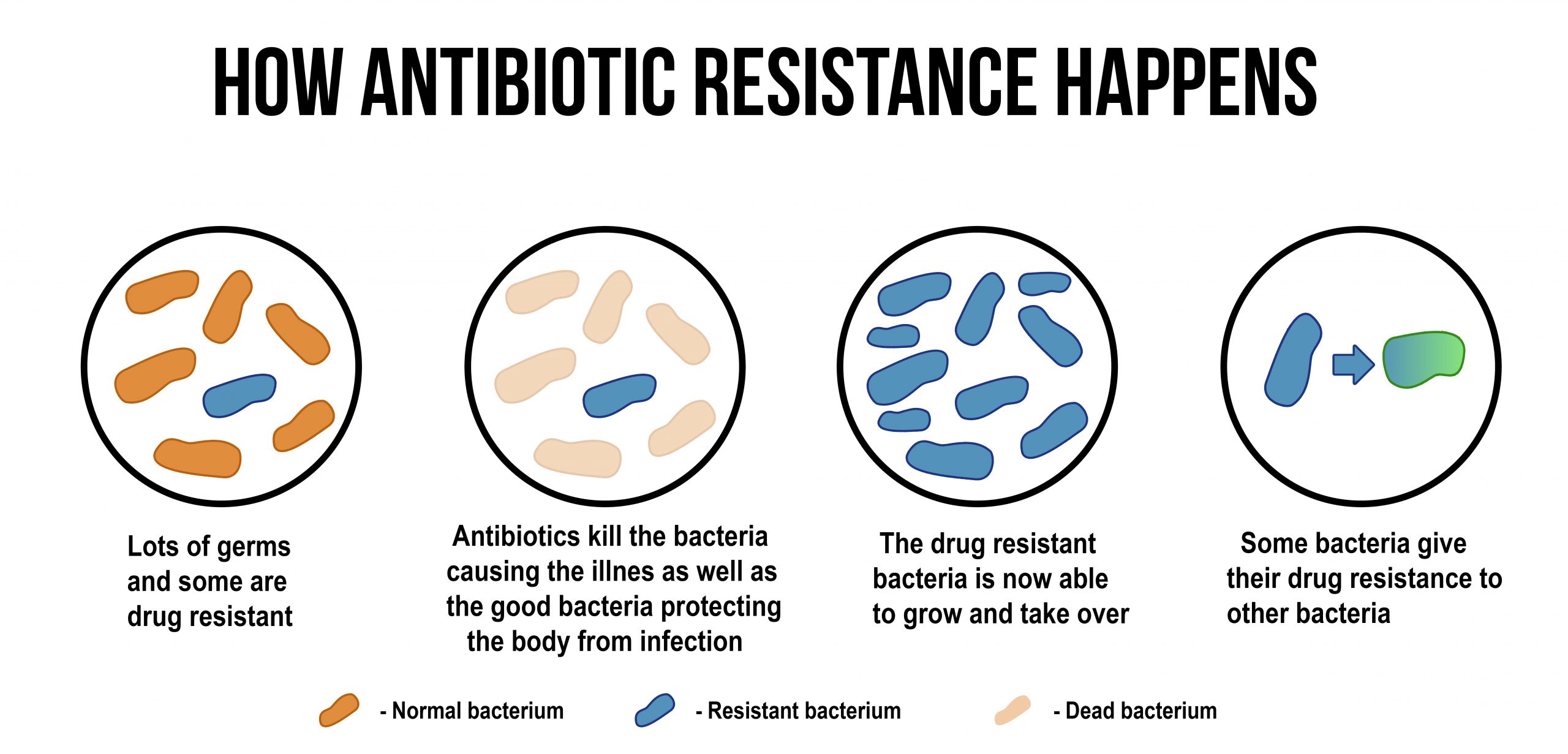
Generic prescription medications can save you a lot of money especially if you don’t have medical insurance.
There are a lot of misunderstandings when it comes to what generic medicines actually are. Let’s clear up a few of these misconceptions so that you can buy generic prescriptions with confidence.
According to the FDA, generic prescriptions have to match the brand name alternative when it comes to their strength, efficacy, side effects, and a variety of other factors. In short, generic medications have to be nearly identical to the costly brand alternatives.
Generic prescriptions are also the majority of prescriptions filled in the United States. Many people use generic prescriptions without realizing that they’re not using the brand name pill.
You can use generic medications for your Healthcare without worrying about compromising on quality. This will help you save money as generic medicines are often far cheaper even if you don’t have insurance.
3. Be Prepared for Medical Emergencies
One of the ways to approach your healthcare is by looking at the two different categories of medical situations that will pop up in our lifetime. There are medical conditions that we can anticipate, and medical emergencies that we need to prepare for.
You can likely anticipate some amount of your general wellness and medical needs. This can range from health problems that are common in your family to routine medical care that almost everyone needs such as dental checkups and preventative care.
However, there are medical conditions that can’t be anticipated. Sudden accidents and illnesses have a way of creeping up without ever being detectable.
Being prepared for medical emergencies can help reduce your costs. This is essential if you do not have health insurance.
Medical preparedness can include everything from having some supplies on hand to help you handle an unexpected injury to making sure you have a plan in place if you have to miss work for an extended period of time.
Not having health insurance doesn’t have to mean that a medical emergency also represents a financial emergency. Planning for an emergency can help reduce the financial burden of a sudden healthcare need.
4. Understand How Insurance Works

Understanding how health insurance works can also help you manage your telemedicine costs even if you don’t plan on getting health insurance in the near future.
Health insurance doesn’t cover all of your medical costs. You also have to pay a monthly premium to keep your health insurance going.
Health insurance also may or may not cover your medical condition or the specific medicines you’re looking to purchase.
A good example of this is CBD and medical marijuana. The issue of whether or not medical marijuana and CBD is covered by health insurance is a complicated one.
Health insurance companies that operate within a single state might be able to cover CBD and other cannabis products. However, current law makes it difficult for national insurance companies to cover these healthcare products.
It’s not just cutting edge treatments that insurance struggles to cover. Many people with health insurance find that they lack adequate access to healthcare.
Telemedicine services offer an effective alternative to traditional healthcare. This can become even more useful if you don’t have insurance but you’re still looking for a reliable way to get the medications that you need.
5. Take Advantage of Telemedicine
Telemedicine offers you a way to get access to doctors, medications, and healthcare services without having to go through all of the lengthy wait times for traditional health care.
There are also telemedicine services that allow you to order medications online. These services even come with access to a doctor that can prescribe you with the medication that you’re looking for.
Telemedicine services also feature shorter wait times. They’re especially effective for people who don’t have insurance who also want to skip the lengthy weights that often come with community health care centers.
Telemedicine programs also operate with a much lower overhead which allows them to reduce costs. You can find a telemedicine program that can let you speak to a doctor in no time at all so you can get the medication you need quickly without having to wait.
You’ve now got five resources that can help you access better telemedicine and healthcare even if you don’t currently have health insurance.
These resources can cover everything from long-term treatment to quick trips to the doctor to get medication for an illness that just popped up.
- Grace Wattikan
Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
Be Prepared for Life’s Unexpected Moments
Youth Preparedness: Teaching, Building, and Coping with Disasters
Educating and preparing your children ahead of time means fewer surprises in the event of an emergency.Growing Up Prepared: Empowering Youth in Disaster Preparedness As we observe National Preparedness Month, it's crucial to remember that disasters can strike at any...
Low-Cost and No-Cost Emergency Preparedness Measures
Small steps today, mean a safer tomorrow for you and your loved ones.Low-Cost and No-Cost Emergency Preparedness So far in our series for National Preparedness Month this September, we've already covered How to Make an Emergency Plan for Your Household and How to...