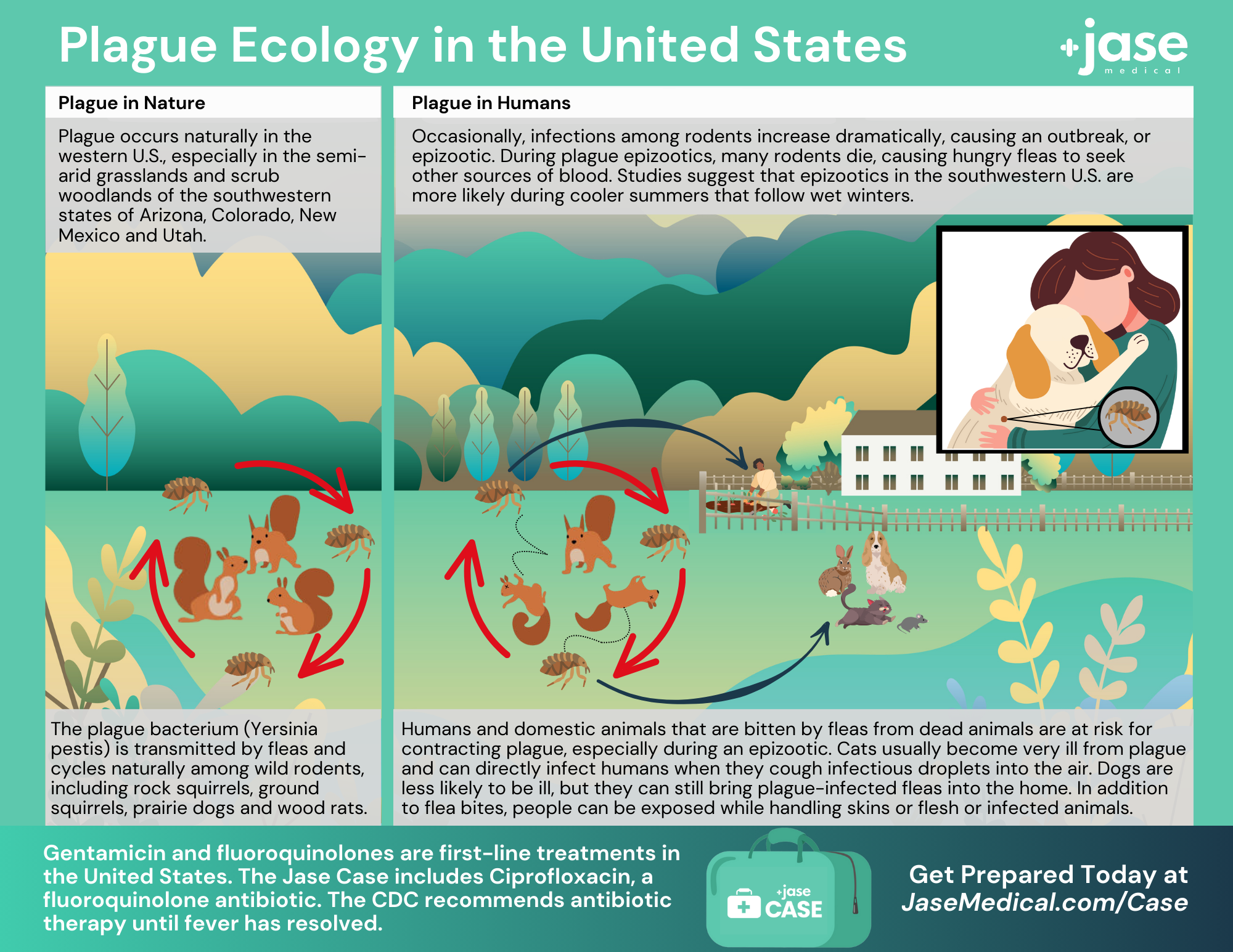
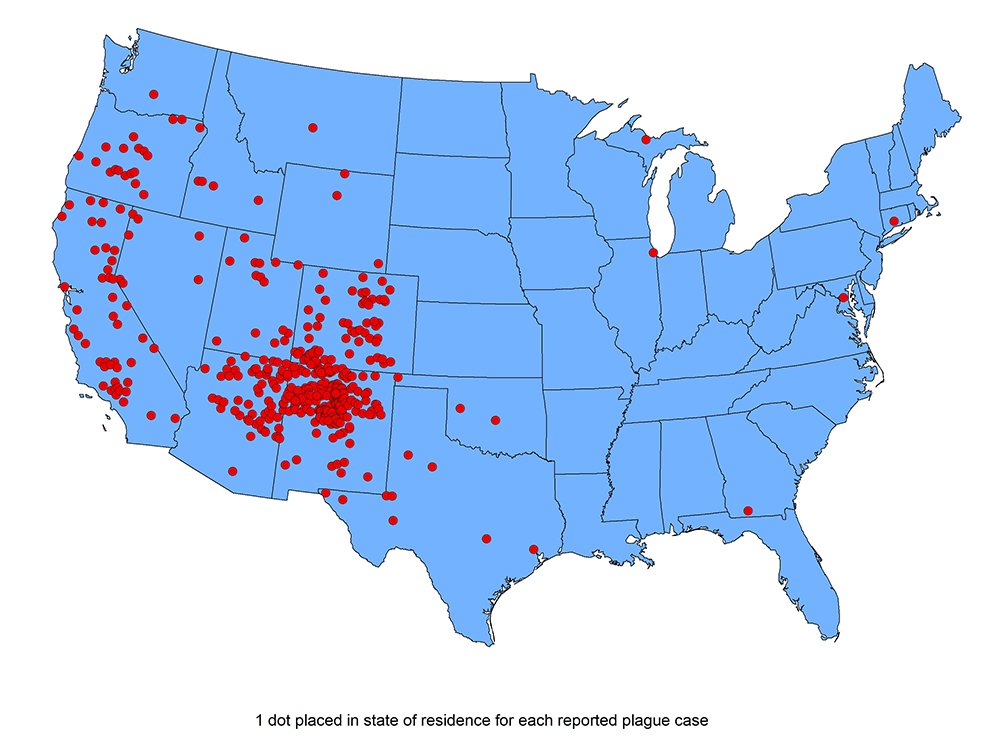
When Disaster Strikes, It’s Not Hunger or Thirst That Takes the First Lives In every disaster zone, from hurricanes in the Caribbean to war zones in Ukraine, the pattern is the same. People worry about food and water, but it’s infection that kills first. A small wound...
Two Simple Ways to Enhance Your Well-being Alongside Medication

“Never go to a doctor whose office plants have died.”
~ Erma Bombeck, humorist and author.

Laughter is said to be the best ‘chronic prescription’ that our Jase Daily service aims to provide. If only. But combining laughter, positive thoughts, and having a purpose in life comes pretty darn close.
We help you get up to a 12-month supply of your medicines. Now, we would like to help you even more by giving you two ideas to combine with your medicines to help you feel even better mentally and physically.
Time is wasting, so let’s get to ‘em.
1. We are more than what we eat: We are also what we think!
Because our thoughts also made us who we are today. So, if you don’t like who you are, and especially how you feel, change your thoughts (“affirmations”). Write down your most negative, crappy, thoughts, and then write underneath each one a positive spin that is realistic and that you can believe.
Doing this is also a great way to replace bad habits with good ones because our thoughts are what hold us back and veers us off the straight and narrow.
Follow these steps before you start thinking yourself to the kind of person you want to be:
A. Do not force it, or overdo it. It’s okay to give yourself permission to mess up now and then. You are a human, not a robot.
B. Make sure they are believable . . . none of those lame unrealistic positive thoughts you read out there.
C. Before you say that you are borderline depressed, or that you are in a funk, first make sure that you are not around the wrong kind of people. You want to be around people who are positive, and make you feel good.
2. Move your body: Go for a walk!
You don’t need to be given a suggestion to go for a walk. That’s just common sense. You know it’s one of the best ways to feel better overall. But the following is a suggestion to get you out there. Because there are days when you just can’t get into gear.
Whenever you tell yourself something like, I don’t feel like it, or you come up with some excuse, tell yourself that you will walk just ten minutes. Then do it. Just go out that door.
What will usually happen is that you will finish what you started, once you get started.
This works, in most cases, even with housework. Do a little something for just a few minutes, like dusting, and you land up doing more! Okay, usually.

Have a Sense of Accomplishment
Very few things can make us feel better than having a sense of accomplishment. You are doing things in your life to feel better, to do better, to be better. It isn’t just about taking prescription medicines, eating right, and going for walks.
What would you like to accomplish?
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
Medical Readiness: What Really Kills First
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole *Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional guidance.* In the evolving...
Be Prepared for Life’s Unexpected Moments
3 Reasons EVERYONE should have emergency medications avaiable. It's all about access—access to medications and care when you need it most. And when things happen outside of your control that access can disappear.Below are 3 examples of how easily this access can be...
Youth Preparedness: Teaching, Building, and Coping with Disasters
Educating and preparing your children ahead of time means fewer surprises in the event of an emergency.Growing Up Prepared: Empowering Youth in Disaster Preparedness As we observe National Preparedness Month, it's crucial to remember that disasters can strike at any...