If you’re considering Jase, chances are you’ve paused and thought, “This makes sense, but I still have a few questions.”You’re not alone. Here are the most common ones we hear, answered plainly. Is this really doctor-prescribed? Yes. Every Jase order is reviewed by a...
Medical Emergency – Heart Attack

Heart disease, a term used to describe a variety of heart conditions, is the number 1 killer of men and women in the US.
Examples of heart disease include:
- High blood pressure
- Angina
- Unstable angina
- Valve disease
- Arrhythmia
- Heart failure
- Congenital and inherited heart conditions
- Coronary artery disease
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction-MI)
Out of all the above conditions, heart attack leads as the number 1 cause of death in men and women in the US.
Every 40 seconds, someone in the United States has a heart attack resulting in about 805,000 people in the United States. Of these, 605,000 are a first heart attack.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack occurs when one of the coronary arteries becomes blocked. The heart muscle is robbed of its vital blood supply and if left untreated, will begin to die because of lack of oxygen.
The more time that passes without treatment to restore blood flow, the greater the damage to the heart muscle.
Causes of heart attack
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the main cause of heart attacks. Coronary arteries send blood to the heart. It is sometimes called coronary heart disease or ischemic heart disease. CAD is caused by plaque buildup in the walls of the coronary arteries. Plaque is made up of deposits of fatty substances, cholesterol, cellular waste products, calcium, and fibrin. As plaque builds up in the arteries, the artery walls become thickened, hard and narrow over time, which can partially or totally block the blood flow. This process is called atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis takes about five years to develop.
Another less common cause is coronary spasm during this coronary spasm, your arteries restrict or spasm on and off, cutting off the blood supply to your heart muscle (ischemia). It can happen while you’re at rest and even if you don’t have serious coronary artery disease. Some causes of coronary spasm are extreme cold, smoking, stress, pain. Cocaine, methamphetamine
Most heart attacks occur when the hardened, built-up plaque shell cracks and ruptures. Platelets, a part of the blood that helps blood clot, come to the ruptured area, and form a clot. If the clot is large enough it can block the artery and block oxygen rich blood from reaching the heart. Without adequate oxygen the heart muscle starts to die, resulting in a heart attack. The hearts’ ability to pump declines depending on where and how much scar tissue develops.
Luckily, most heart attacks are survivable, with about a 90 percent survivability rate. These statistics are due to early intervention and prevention awareness.
Symptoms can vary between men and women
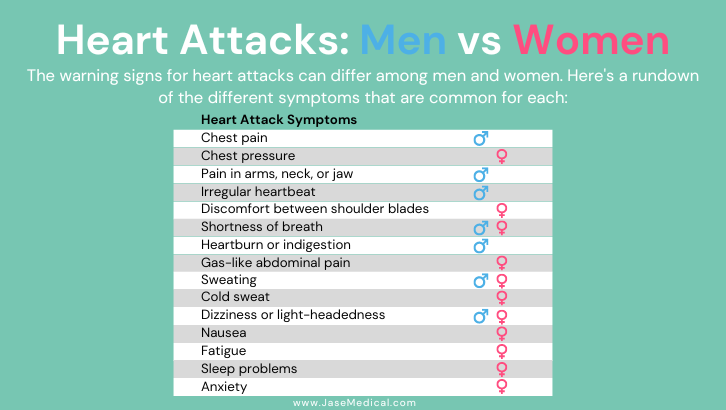
Symptoms of an impending heart attack can manifest up to a month to days and even hours before. Symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Abdominal pain
- Sweating
- Swelling in Legs, Ankles, and Feet
- Heart Palpitations
Symptoms of heart attack in progress
- Uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness or pain in the center of your chest. It lasts more than a few minutes or goes away and comes back.
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw or stomach.
- Shortness of breath with or without chest discomfort.
- Other signs such as breaking out in a cold sweat, nausea or lightheadedness
- About 1 in 5 heart attacks are silent—the damage is done, but the person is not aware of it.
What to do if heart attack suspected- ACT QUICKLY
- Call 911 immediately, quick intervention is key to survival- if in doubt, call. Many people avoid calling until heart attack is well under way.
- Aspirin or no aspirin? Don’t give aspirin unless directed by emergency personnel or care provider. There are several reasons not to give aspirin, one being the increased risk of bleeding, another is allergy to aspirin and even interaction with other medications.
- Keep calm, reassure patient, stay with them until help arrives
- If the person is unconscious, no pulse and/or not breathing, initiate CPR, continue until help arrives. Brain death occurs 10 minutes after 10 minutes with no oxygen
- If a defibrillator (AED) is available hook up patient and follow prompts- remove patient from liquid, metal surfaces and to a safe area. Know how and when to use the AED through previous training. A heart attack can spiral into a sudden cardiac arrest. If the patient has a pacemaker, do not apply pads directly over the pacemaker. Also do not apply pads over medical patches.
How heart attack diagnosed
- Blood test- troponin level measures the amount of proteins in the blood. During a heart attack, heart muscle cells die and release proteins in the bloodstream.
- EKG measures the electrical activity of the heart
- Heart imaging tests such as cardiac CT scan
Risk factors for heart attacks
Note: Risk factors are the same for silent heart attacks as their symptomatic counterparts
- Brush your teeth, get regular dental exams-The link between periodontal pathogens and cardiovascular disease (CVD) Recent studies have linked periodontal pathogens with atherosclerotic plaque in 80% of specimens, meaning that periodontal bacteria (among others) were identified in 80% of plaque in carotid artery specimens. (Atherosclerotic plaques leading to atherosclerosis)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetic– adults with diabetes are twice as likely to have a heart attack or stroke
- Smoker
- Overweight
- Physical inactivity
- Genetic predisposition
- Stress, especially chronic stress
- Even young and healthy population can experience heart attack
Prevention
Lifestyle
- Manage and reduce stress- Deep breathing, therapy, talking to friends and loved ones can significantly reduce and manage stress
- Maintain healthy cholesterol levels through diet, exercise and stress management
- Exercise regularly- consult your care provider regarding type, how often and how much exercise
- Healthy diet-eliminate sugar, consult with your provider the ideal diet for you and your preexisting diagnosis and meds.
- Quit smoking- smoking constricts blood vessels, and chemicals in cigarettes can cause the blood to thicken and form clots.
- Brush teeth twice a day, replace toothbrushes as needed. Oral bacteria has been found in the fatty deposits of people with atherosclerosis.
- Drink your water! Dehydration can cause your heart to beat faster, cause an irregular heartbeat or even palpitations. In addition, dehydration makes your blood thicker and constricts blood vessel walls. This can cause high blood pressure and put strain on your heart.
Meds
Along with preventative lifestyle choices it may be necessary to add medication(s). Some of these include:
- Over the counter meds such as aspirin- consult provider before using
- Beta blockers-some examples include- atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol XL) propranolol (Inderal). Beta-blockers-block the effects of adrenaline, which comes on in response to stressful situations.
- Ace inhibitors- some examples include- benazepril (Lotensin), captopril (Capoten), enalapril-(Vasotec), fosinopril (Monopril), lisinopril (Zestril and Prinivil), qinapril (Accupril), ramipril (Altace). ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors prevent the body from producing the artery-constricting hormone angiotensin. Arteries relax with ACE inhibitors which in turn lowers blood pressure.
- Prescription blood thinners-examples include warfarin, clopidogrel
- Statins- some examples include atorvastatin (Lipitor), fluvastatin (Lescol XL), lovastatin (Altoprev), pitavastatin (Livalo), pravastatin (Pravachol- Statins lower LDL cholesterol, reduce inflammation.
- Brooke Lounsbury, RN
Medical Content Writer
Lifesaving Medications
Recent Posts
Keeping you informed and safe.
FAQ: Our most commonly asked questions about Jase
Medical Readiness: What Really Kills First
When Disaster Strikes, It’s Not Hunger or Thirst That Takes the First Lives In every disaster zone, from hurricanes in the Caribbean to war zones in Ukraine, the pattern is the same. People worry about food and water, but it’s infection that kills first. A small wound...
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole
Exploring Dr. William Makis’ Hybrid Orthomolecular Cancer Protocol: Focus on Ivermectin and Mebendazole/Fenbendazole *Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional guidance.* In the evolving...



